I do not usually cover tragic stories, however I used to live in this area and this story hit me hard and I know affects the community greatly. My goal is to help educate the events of this tragedy, to help better understand why the community has been so impacted.
Setting the Scene: October 20, 2024 – Fall City, Washington
The Humiston family lived at 7715 Lake Alice Road SE, a two-story, single-family home nestled in a quiet, suburban neighborhood of Fall City, Washington. Surrounded by lush evergreens and sitting on a half-acre lot, the property exuded tranquility—ideal for a growing family.
The home was purchased in 2018 by Mark and Sarah Humiston from a couple who had lived there for nearly two decades.
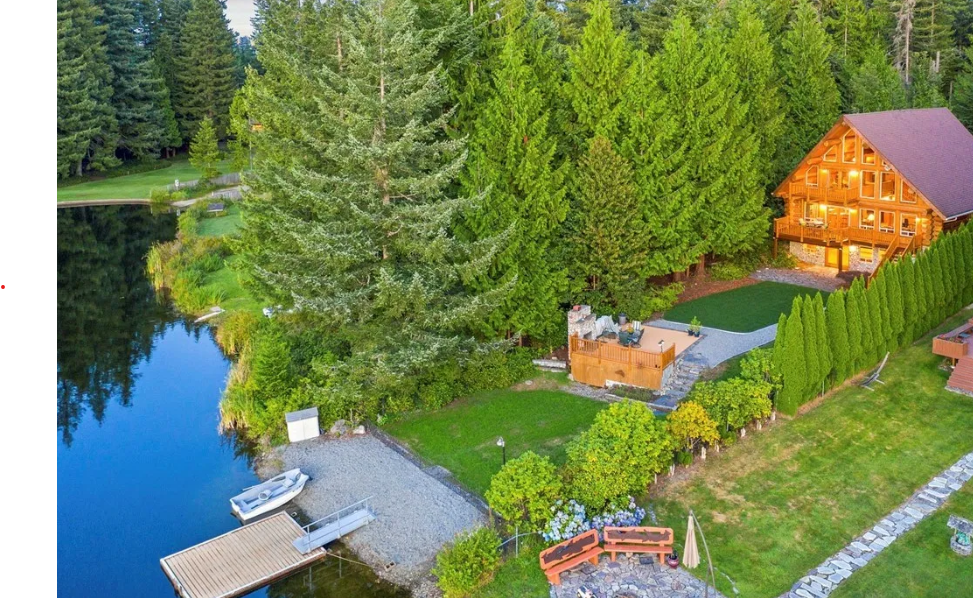

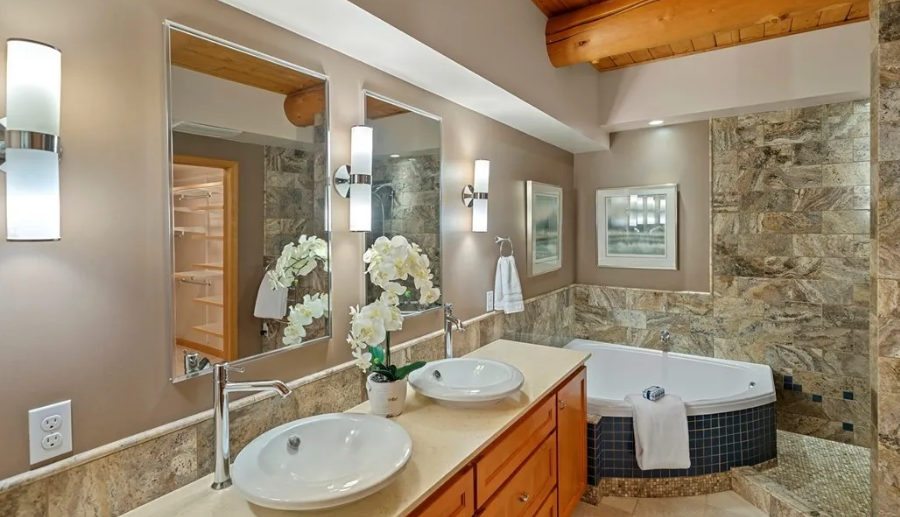
The four-bedroom, three-bathroom house was built in the late 1990s, boasting hardwood floors, a fireplace in the family room, and an expansive basement-level family area. The master bedroom, located upstairs, featured an ensuite bathroom, which would later become the site of Sarah Humiston’s tragic final moments.

In addition to the ample interior space, the home’s large backyard backed into a wooded area, creating a sense of privacy.
The neighborhood of Lake Alice Road SE was known for its quiet, family-friendly atmosphere, with neighbors rarely locking their doors and children riding bicycles along the winding streets. To many in the community, the Humiston house symbolized the idyllic life that Mark and Sarah had hoped to build for their five children—until the unimaginable events of October 21, 2024, transformed it into the scene of a horrific tragedy.
This family of seven included Mark and Sarah Humiston—the parents—and their five children: Andrew Jacob Humiston (15 years old), Benjamin Humiston (13 years old), Joshua Humiston (9 years old), Katheryn Humiston. (7 years old), and B.A.H. (11 years old). By all outward appearances, the Humistons were a close-knit, devoted family. Mark Humiston worked as an electrical engineer at Hargis Engineers in Seattle.

Mark’s dedication to his career at Hargis Engineers helped support the family, while his wife, Sarah Humiston, focused on managing the household.
Sarah was a registered nurse, though her nursing license expired at the end of 2022, suggesting she had taken a step back from her career to focus on homeschooling the couple’s five children.

Mark and Sarah’s decision to homeschool their children reflected their deep commitment to their family’s values and education. Despite being homeschooled, the children were active within the Fall City community and well-known to neighbors. The family often participated in local events, and the children were frequently seen riding bikes or playing outdoors, a fact confirmed by several community members. Neighbors described the Humiston children as polite and well-adjusted, often attending community gatherings and becoming familiar faces around the neighborhood.
On the night of October 20th, nothing seemed particularly out of the ordinary. The younger children went to bed in their shared rooms, and Mark and Sarah retired to the master bedroom. But unknown to them, Andrew had made a decision that would shatter the family forever.
Prelude to the Tragedy: A Teen on the Edge
From the outside, Andrew Jacob Humiston appeared to be a typical 15-year-old living with his family in Fall City, Washington. However, beneath the surface, Andrew harbored growing resentment toward his parents and siblings. As the eldest of five children, Andrew had responsibilities that he neither asked for nor embraced. While the younger siblings thrived in their homeschool environment, Andrew saw his own academic performance decline steadily over the past year. Instead of addressing his difficulties head-on, Andrew withdrew from his family and spent most of his time in his room, disengaged from their daily activities.

Mark and Sarah Humiston tried to hold their son accountable, but Andrew refused to meet their expectations. His parents weren’t harsh, but they expected their children to do well. Mark, a dedicated electrical engineer at Hargis Engineers, worked hard to provide for the family and hoped his eldest son would grow into a responsible young man. Sarah, a former nurse who had shifted her focus to homeschooling their children, took the lead in educating and disciplining the children, especially Andrew. Despite her efforts, Andrew consistently fell short—not only in his schoolwork but also in basic household responsibilities.
Rather than try to improve, Andrew grew resentful of the structure his parents provided, viewing their guidance as punishment. The other children seemed to thrive, which only deepened his sense of failure. In his mind, his siblings were treated better and were more loved—a belief that fed his growing bitterness. Instead of seeking help or trying to improve his situation, Andrew blamed his family for his unhappiness, convinced that they were the source of all his frustrations.
Escalating Tensions
The Humiston household was not without conflict, but Andrew’s behavior in the months leading up to the murders had become increasingly troubling. On more than one occasion, Sarah caught Andrew shirking his schoolwork, opting instead to spend time online or playing video games. Things took a serious turn when Sarah discovered that Andrew had been viewing pornography—an incident that resulted in a tense confrontation with both parents. While Mark tried to approach the situation calmly, Sarah’s disappointment in Andrew was palpable. She had invested her time and energy in raising and teaching him, and this latest incident felt like a betrayal.

Andrew didn’t take the confrontation well. Instead of apologizing or taking responsibility for his actions, he retreated further into his resentment. Friends would later report that Andrew felt like the black sheep of the family, harboring a belief that he was unfairly targeted by his parents. The truth, however, was that his parents were doing their best to help him, even if Andrew refused to see it that way.
In Andrew’s mind, he was the victim, and everyone else—his parents, his siblings, and even the world—was to blame for his failures. His refusal to accept responsibility fueled an internal rage, one that quietly simmered beneath the surface.
A Dangerous Plan Takes Shape
Rather than try to change or seek help, Andrew began to devise a plan that would solve his problems the only way he knew how—by eliminating his family. Investigators would later uncover online searches on Andrew’s devices that revealed his growing fascination with crime scenes, firearms, and staged suicides. He knew where his father’s Glock pistol was kept—inside a locked gun box near the front door—and, crucially, he was the only one who knew the combination.

The plan was cold, calculated, and deliberate. Andrew decided that he would kill his entire family and frame his younger brother, Benjamin Humiston, by staging the crime scene to look like a murder-suicide. To Andrew, this wasn’t just about getting revenge—it was about freedom. In his twisted mind, eliminating his family would finally give him the control he craved, allowing him to escape the disappointment, discipline, and accountability he resented so much.
In the days leading up to the murders, Andrew acted as though everything was normal, giving no outward sign of the violence he was about to unleash. He didn’t appear remorseful or conflicted. If anything, he seemed more detached than usual, as though he had already emotionally severed himself from his family.
October 21, 2024 – The Night of Horror
At around 4:30 AM, Andrew retrieved the Glock pistol from the lockbox. Armed and prepared, he methodically began his plan to eliminate his entire family.
The Shooting of B.E.H.: A Survivor’s Nightmare
The night of October 21, 2024, began with 15-year-old Andrew Jacob Humiston systematically targeting his family. One of his first stops was the bedroom of his 11-year-old sister, B.E.H., the only child who would survive the attack. She was alone in her room when her brother entered, pistol in hand.

The room was filled with the trappings of childhood—stuffed animals, brightly colored blankets, and schoolwork tucked into drawers—an innocent space soon to be forever tainted by unspeakable violence.
B.E.H. was likely asleep when Andrew approached, but the sound of his footsteps must have stirred her awake. Before she could react, Andrew raised his father’s Glock pistol and fired the first shot, striking her in the neck. The bullet tore through soft tissue, narrowly missing critical arteries, but caused severe bleeding. In an instinctive attempt to shield herself, B.E.H. raised her hand—but Andrew fired a second shot, hitting her hand and shattering bones.

The pain was excruciating, but B.E.H. knew her only chance at survival was to stay silent. Despite the overwhelming shock and pain, she played dead, lying perfectly still on the blood-stained bed. Andrew, assuming she was dead, left the room without checking. His footsteps receded down the hall, leaving B.E.H. alone but alive, bleeding heavily from her wounds.

The Basement Murders: Mark, Joshua, and Katheryn Humiston
After shooting B.E.H., Andrew made his way to the basement. The lower level of the house served as both a family space and temporary sleeping quarters for Mark Humiston, his 9-year-old son Joshua, and 7-year-old daughter Katheryn.

All three were located at the bottom of the basement stairs when Andrew arrived.

Mark Humiston: Shot Trying to Protect His Family
Mark, an electrical engineer at Hargis Engineers, was lying on the couch when Andrew entered the basement. The first shot grazed Mark’s left shoulder, likely startling him awake. Before he could fully rise or comprehend what was happening, Andrew fired two more shots—one struck Mark’s left armpit, and the other penetrated his lower back.
Mark was still alive, but gravely injured, as he collapsed onto the floor. As he struggled to move, Andrew fired a fourth and final shot—this time into Mark’s neck, causing catastrophic injuries. Blood pooled beneath him as he lay dying on the basement floor, unable to protect the children who were with him.

Katheryn Humiston: Innocence Lost
Just steps away from her father was Katheryn Humiston, a 7-year-old girl whose life ended in an instant. Andrew shot her in the head, killing her instantly. The bullet entered the side of her skull, ensuring that she had no chance to escape or cry for help. Katheryn’s small body crumpled near the base of the basement stairs, next to the father who had tried to protect her.
The Killing of Joshua Humiston: A Tragic End
Also in the basement was 9-year-old Joshua Humiston, another target in Andrew’s carefully planned attack. Andrew fired a single shot at Joshua’s forehead, the bullet traveling through his skull and exiting through the back. Joshua was killed instantly, his body collapsing beside his sister and father. The basement, once a place of family gatherings, had now become a scene of horror.

Staging the Crime Scene: Framing Benjamin
As the sound of gunfire echoed through the basement, 13-year-old Benjamin Humiston—another of Andrew’s younger brothers—came rushing toward the noise. Investigators later determined that Benjamin Humiston must have heard the shots and ran to the basement to see what was happening.

When Andrew saw his brother enter the room, he raised the Glock pistol and fired twice. The first shot struck Benjamin Humiston in the left cheek, causing massive facial trauma as the bullet passed through soft tissue. The second shot entered behind his right ear, traveling diagonally through his brain and lodging in his skull. Death was almost immediate.

With his father, brother, and sister dead, Andrew began to stage the scene to make it appear as if Benjamin had committed the murders. He placed the Glock pistol in Benjamin’s hand, intending to deceive investigators into believing the crime was a murder-suicide. But forensic evidence would later reveal the truth. Investigators found no gunpowder residue or blood transfer on Benjamin, and the angle of the wounds did not align with a self-inflicted gunshot. Andrew’s attempt to shift the blame onto his brother failed.
Investigators would later discover several inconsistencies:
- The absence of blood transfer on the gun suggested that Benjamin Humiston had not fired the weapon.
- No stippling (burn marks) was found around the wounds, meaning the shots were fired from a distance—inconsistent with a self-inflicted gunshot wound.
- Ballistics evidence showed that the bullet trajectories did not align with the angle expected for a suicide.
Despite Andrew’s attempt to mislead investigators, the forensic evidence quickly pointed to him as the true perpetrator. The staged scene, while methodical in its intent, was insufficient to deceive trained investigators.
A Basement of Tragedy
The basement, which had once been a space for family time and quiet evenings, was now a devastating crime scene. The lifeless bodies of Mark, Joshua, Katheryn, and Benjamin lay in pools of blood, surrounded by spent shell casings and blood spatter. The basement walls bore silent witness to the brutality and cold precision with which the murders were carried out.

By the time Andrew left the basement, he had killed four members of his family. The violence was far from over—only his mother remained, unaware of the horror that had unfolded below.
By the time he climbed the stairs and left the basement, Andrew had already killed four members of his family. Only his mother remained.
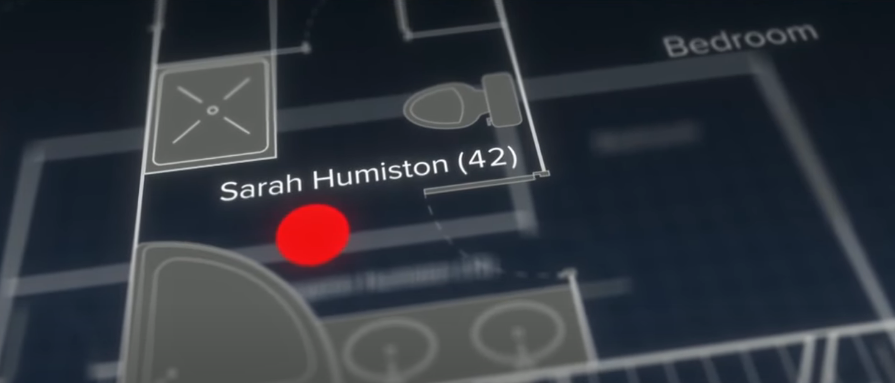
The Final Victim: Sarah Humiston (Mother)
Andrew’s final target was his mother, Sarah, who was asleep upstairs in the master bedroom. When Sarah heard the gunshots, she locked herself in the bathroom. But Andrew was determined to complete his plan. He kicked open the bathroom door, splintering the frame, and found Sarah cowering near the bathtub.

He fired multiple shots at close range. One bullet entered behind her right ear and exited through her cheek. Another bullet struck her in the left temple, lodging behind her eye. Sarah collapsed to the floor, her body folded forward in a pool of blood.
The 911 Calls: A Confession and a Plea for Help
At approximately 4:55 AM, Andrew called 911 from inside the house. Out of breath, he told the dispatcher, I just shot my whole family, and my brother killed them too and took himself out. In a rambling, confused manner, Andrew tried to frame his brother Benjamin Humiston as the murderer, insisting that his brother had killed everyone before turning the gun on himself. Andrew stayed on the line with the dispatcher, hiding in the bathroom on the main floor of the house.
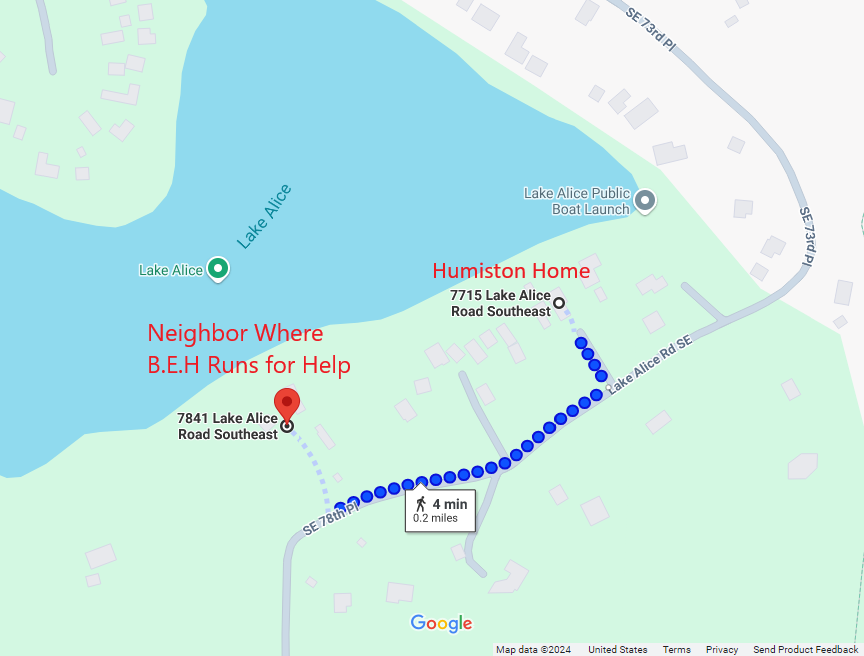
Meanwhile, at 5:02 AM, Bradley Dennis, a neighbor, called 911 after B.A.H. showed up at his door. The 11-year-old girl, bleeding from her neck and hand, had escaped through a fire window in her bedroom and ran down to his house.

Frantically rang the doorbell, screaming that her brother Andrew had killed their family. Bradley brought her inside and contacted the authorities, confirming that Andrew was still at the family home and likely armed.
Police Arrival and Arrest
As officers from the King County Sheriff’s Department arrived at the Humiston home in the early morning hours of October 21, 2024, they found 15-year-old Andrew Jacob Humiston waiting in the driveway. Whether he intended to surrender or was simply lingering outside remains unclear. Andrew offered no resistance when officers approached and was arrested without incident.
Meanwhile, deputies entered the house to search for survivors. What they found inside was a scene of unimaginable horror. Mark, Joshua, Katheryn, and Benjamin Humiston lay dead—shot execution-style—while B.E.H., Andrew’s 11-year-old sister, had miraculously escaped and alerted a neighbor.
Andrew was taken into custody at the scene, and officers quickly determined that his initial claim—that his brother Benjamin was responsible—was a fabrication. The evidence did not align with a murder-suicide scenario, and Andrew soon became the primary suspect in the investigation.
The Survivor’s Testimony
At the hospital, B.A.H. was treated for her gunshot wounds and provided a detailed statement to detectives. She described in vivid detail how Andrew systematically killed their family, shot her and her sister, and left her for dead. Her testimony corroborated the forensic evidence and disproved Andrew’s attempt to frame his brother.
Conclusion: A Tragic and Premeditated Crime
The Humiston family murders were a shocking and premeditated act of violence, carried out by 15-year-old Andrew Jacob Humiston. His attempt to manipulate the crime scene and deceive investigators failed due to the survivor’s testimony and forensic analysis. The murders left behind a devastated community and a tragic story of a young boy who made the unimaginable decision to destroy his family.
Now facing 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree and 1 count of Attempted Murder, Andrew Jacob Humiston stands at the center of a high-stakes legal battle that will determine whether he is tried as a juvenile or adult, and whether the justice system will seek rehabilitation or punishment for his horrific actions.
Full Case Overview
Here, I will go over all the details I have learned about the case during my investigation.
- Charges:
- Aggravated Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence) – 5 counts
- Attempted Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence) – 1 count
Details of the Charges
Count 1: Aggravated Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: Sarah M. Humiston (Mother)
- Date of Incident: October 21, 2024
- Description:
The respondent, Andrew Jacob Humiston, with deliberate and premeditated intent, caused the death of his mother, Sarah Humiston. The charge includes the aggravating factor that the crime was part of a coordinated scheme targeting multiple family members. It is further compounded by the relationship between the respondent and the victim, as Sarah was his mother, falling under domestic violence provisions as defined by RCW 10.99.020. Evidence suggests Sarah was found in the master bedroom’s ensuite bathroom, with multiple gunshot wounds, one of which exited through her cheek. Blood spatter and a large pool of blood on the floor indicate that she was attacked at close range.
Count 2: Aggravated Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: Benjamin Humiston (Male, Brother, DOB: May 29, 2011)
- Description:
Andrew Humiston allegedly murdered his younger brother, Benjamin Humiston, as part of the same scheme. Investigators found Benjamin Humiston’s body staged to make it appear as though he had killed the other family members before committing suicide. However, forensic evidence, including bullet trajectories and lack of stippling around entry wounds, revealed that Benjamin Humiston was also a victim. The forensic pathologist determined that the wounds could not have been self-inflicted, and the Glock pistol placed in his hand was inconsistent with the lack of blood transfer on the weapon.
This false staging attempt was intended to mislead investigators and conceal Andrew’s responsibility. The murder was carried out with intent and in conjunction with the murders of other family members, further supporting the aggravating circumstances charge.
Count 3: Aggravated Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: Joshua Humiston (Male, Brother, DOB: May 1, 2015)
- Description:
Joshua Humiston, the 9-year-old brother, was found lying at the bottom of the stairs along with their father, Mark. Autopsy reports indicate that he suffered a gunshot wound to the forehead, with the bullet exiting through the back of his skull. This wound suggests a close-range execution, and blood patterns reveal that he likely did not move after being shot. Joshua Humiston was among the younger victims, and the premeditated nature of the crime underscores the severity of this charge. The act falls under domestic violence, given that the respondent was a sibling, and the attack was part of the broader plan involving multiple victims.
Count 4: Aggravated Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: Mark M. Humiston (Father)
- Description:
Mark Humiston, the respondent’s father, was found partially lying across the legs of his son Joshua Humiston at the bottom of the basement stairs. The autopsy revealed four gunshot injuries: one grazing wound to the shoulder, two penetrating gunshot wounds to the back, and one fatal shot to the lower neck. Investigators believe the attack on Mark was deliberate and aimed to prevent him from interfering with the other murders. Blood spatter analysis and the location of Mark’s body suggest he was attacked from behind. Mark’s murder is treated as aggravated because it was committed with intent and was part of a larger coordinated scheme involving the deaths of multiple family members.
Count 5: Aggravated Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: Katheryn Humiston. (Female, Sister, DOB: October 10, 2017)
- Description:
Katheryn Humiston., the 7-year-old sister, was killed with a single gunshot wound to the head. The projectile traveled from left to right across her skull, causing severe brain trauma and lacerations. B.A.H., another sibling who survived, testified that she saw Andrew shoot Katheryn Humiston. and that she witnessed her sister fall after the shot. The young victim’s age and the deliberate targeting of children within the family further elevate the seriousness of this charge.
The crime against Katheryn Humiston. is also categorized as domestic violence, given that Andrew was her brother. This murder was part of the coordinated effort to kill all members of the household.
Count 6: Attempted Murder in the First Degree – Domestic Violence
- Victim: B.A.H. (Female, Sister, DOB: April 12, 2013)
- Description:
Andrew Jacob Humiston is also charged with the attempted murder of B.A.H., his 11-year-old sister, who managed to survive the attack. According to her testimony, Andrew shot her in the hand and neck. She pretended to be dead to avoid further harm. B.A.H. recalled seeing her brother walk around the house, making a phone call after the shootings. She took the opportunity to escape through a window and fled to the nearby home of Bradley Dennis, where she sought help.
The fact that Andrew deliberately aimed to kill B.A.H. but failed to do so resulted in an attempted murder charge. This act is also classified as domestic violence due to the familial relationship.
Additional Aggravating Factors
Each count carries an aggravated designation under RCW 9A.32.030 and RCW 10.95.020 due to the following factors:
- Multiple Victims: The murders were part of a coordinated plan targeting the entire family.
- Premeditation: The planning and staging of the crime demonstrate clear intent.
- Staged Crime Scene: Andrew attempted to manipulate the crime scene to make it appear as though Benjamin Humiston had committed the murders and then taken his own life.
- Use of a Firearm: A Glock pistol was used to carry out the killings and the attempted murder.
These factors contribute to the severity of the charges, with each act reflecting a premeditated attack on multiple family members. The domestic violence designation further underscores the relational dynamics and emotional impact of the crime.
Incident Summary
Timeline of Events
On October 21, 2024, at approximately 4:55 AM, a chilling 911 call was received from a male, later identified as Andrew Jacob Humiston. During the call, Andrew confessed that he had shot his entire family and claimed that his brother, Benjamin Humiston, had killed everyone before taking his own life. Andrew was reported to be hiding in the bathroom on the main floor of the house during the call.
During the 911 conversation, Andrew mentioned that he had been afraid of getting into “a lot of trouble” due to recently being caught looking at pornography, which he suggested was a possible motive for his actions. He emphasized his fear that everyone would be angry with him and seemed to express regret, but in a manner that further complicated the case with conflicting narratives about the sequence of events.
At 5:02 AM, a second 911 call was made by Bradley Dennis, a neighbor who lives approximately a quarter-mile away. Bradley reported that an 11-year-old girl, B.A.H., had arrived at his home, frantically ringing the doorbell. B.A.H. informed him that her family had been shot and that she believed she was the only survivor. Bradley described her injuries as a gunshot wound to her neck and hand, and she was bleeding profusely.
B.A.H. explained to Bradley and the dispatcher that she saw Andrew Humiston shoot their siblings and parents and that he was the one responsible for the murders. She told the dispatcher that Andrew may still be at the family home and warned that he could have a gun. B.A.H.’s testimony provided critical insights into the sequence of events and cast doubt on Andrew’s initial claim that Benjamin Humiston was responsible for the murders.
The Crime Scene
When deputies from the King County Sheriff’s Office arrived at the residence located at 7715 Lake Alice Rd SE, Fall City, Washington, they secured the perimeter and cautiously entered the home. Inside, they discovered a gruesome scene that matched B.A.H.’s description.
- Location of Victims:
- Mark Humiston (Father) – Found at the bottom of the stairs with his body partially lying over his son Joshua Humiston
- Joshua Humiston (Brother, 9 years old) – Also found at the bottom of the stairs, lying beneath his father.
- Katheryn Humiston. (Sister, 7 years old) – Found slumped over in the hallway, not far from the stairs.
- Benjamin Humiston (Brother, 13 years old) – Discovered with a gunshot wound, staged to appear as though he had shot the others and then killed himself.
- Sarah Humiston (Mother) – Located in the ensuite bathroom of the master bedroom, surrounded by a pool of blood.
Investigators noted blood spatter patterns throughout the home, consistent with multiple gunshots fired in close quarters. The bodies of Mark, Joshua Humiston, and Katheryn Humiston. were clustered near the bottom of the stairs leading to the daylight basement, suggesting they were attacked as they tried to flee or were deliberately targeted there.
In the master bedroom’s ensuite bathroom, Sarah’s body was found folded forward on the floor, with several gunshot wounds. The doorframe to the bathroom was splintered, indicating it had been forced open. Blood stains and bullet holes were observed on the back of the bathroom door, along with a single spent 9mm shell casing found near the sink.
Staging of the Crime Scene
Deputies quickly realized that the crime scene had been staged to mislead investigators. Andrew’s brother, Benjamin Humiston, had been deliberately positioned to suggest that he was the shooter. A Glock handgun was placed in Benjamin Humiston’s hand, and the arrangement of the bodies implied that Benjamin Humiston had killed the family before taking his own life. However, forensic evidence, including the trajectory of gunshot wounds and the absence of blood transfer on the weapon, contradicted this narrative.
Investigators determined that Andrew had carefully staged the scene to shift blame onto his brother, in an attempt to create a false narrative of a murder-suicide. Andrew even repeated this fabricated story during his initial 911 call, claiming that Benjamin Humiston was responsible for the killings.
Testimony from B.A.H. (The Survivor)
The surviving sibling, B.A.H., provided critical testimony during her forensic interview at the Harborview Medical Center. B.A.H. described in vivid detail how she and her younger sister, Katheryn Humiston., had been asleep in their shared room when they were awoken by the sound of gunshots. She saw Andrew enter the room with a silver Glock pistol, which she identified as her father’s firearm.
According to B.A.H., Andrew shot her in the hand and neck. Believing she was dead, he left the room. B.A.H. recalled seeing Andrew talking on the phone in another room, giving her the opportunity to escape. She described using the “fire window” in her room to climb outside and run to the Dennis family home for help.
In her interview, B.A.H. revealed that Andrew had recently struggled at school, and his fear of getting in trouble for failing tests was weighing heavily on him. She also disclosed that Andrew was the only sibling with access to the lockbox containing the Glock pistol, a key detail that tied him to the crime.
Motive and Psychological Context
Andrew mentioned during his 911 call that his actions were influenced by his fear of getting into trouble, particularly after being caught looking at pornography. His emotional state appeared unstable, and investigators believe that stressors at school and fear of consequences at home might have contributed to his decision to commit the murders. However, the calculated nature of the crime, the staging of the scene, and the systematic elimination of family members suggest premeditation rather than an impulsive act.
Autopsy and Forensic Evidence
The King County Medical Examiner’s Office conducted autopsies on October 22 and 23, 2024. Key findings include:
- Mark Humiston (Father): Four gunshot wounds, including two penetrating injuries to the back.
- Joshua Humiston (9-year-old brother): Single fatal gunshot wound to the forehead.
- Katheryn Humiston. (7-year-old sister): Shot in the head, with bone fragments causing brain damage.
- Sarah Humiston (Mother): Multiple gunshot injuries, including one that pierced her face.
- Benjamin Humiston (13-year-old brother): Two gunshot wounds, staged to appear as self-inflicted.
The absence of stippling on some wounds indicated that shots were fired from a distance, refuting the staged murder-suicide scenario involving Benjamin Humiston Additionally, aspirated blood found in the victims’ lungs suggested they were alive for a brief period after being shot, further supporting the argument that the attacks were deliberate and calculated.
Police Investigation and Arrest
After the crime scene was secured, Andrew was arrested without resistance. He was transported to the Sammamish Police Station, where he was offered an opportunity to speak with detectives. However, after consulting with an attorney, Andrew declined to make any statements.
The police obtained a judicially authorized search warrant for a detailed investigation of the residence. Among the items discovered were an open gun lockbox near the front door and a pistol holster, both empty. This further corroborated B.A.H.’s statement that the Glock pistol used in the shootings had come from the lockbox, to which only Andrew had access.
Conclusion
The investigation revealed that Andrew Jacob Humiston, a 15-year-old, systematically executed a plan to murder his entire family, staging the crime scene to frame his brother, Benjamin Humiston, for the murders. His premeditated actions, including his attempt to mislead law enforcement through the staged scene and false statements during the 911 call, demonstrate a high level of intent and calculation.
The forensic evidence, survivor testimony, and police investigation leave no doubt about Andrew’s responsibility for the killings. As a result, he faces 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree and 1 count of Attempted Murder in the First Degree, all classified under domestic violence provisions.
Crime Scene and Investigation Findings
Location and General Overview of the Scene
The crime took place at the Humiston family home, located at 7715 Lake Alice Rd SE, Fall City, Washington, in an unincorporated area of King County. Deputies from the King County Sheriff’s Office arrived on the scene shortly after receiving two 911 calls: one from Andrew Jacob Humiston and another from Bradley Dennis, a neighbor.
Upon entering the residence, deputies were confronted with a horrific and chaotic crime scene, with the bodies of several family members distributed across the basement level and master bedroom. Investigators determined that multiple gunshots had been fired throughout the house, and the scene was marked by large pools of blood, scattered bullet casings, and blood spatter on walls, floors, and doors.
Detailed Findings from Key Locations in the House
The Entryway and Main Floor
- Upon entering the front door, deputies observed an open gun lockbox and a pistol holster on a bench near the door. Both the lockbox and holster were empty, which suggested that the Glock pistol used in the murders had been taken from the box.
- Andrew Humiston was found hiding in the bathroom on the main floor when deputies arrived. He did not resist arrest, and deputies detained him without further incident.
The Stairwell to the Daylight Basement
- The bodies of Mark Humiston (father) and Joshua Humiston (9-year-old brother) were found at the bottom of the stairs that led to the daylight basement. Mark was partially lying across the legs of Joshua Humiston, suggesting that they had been attacked while either fleeing or protecting each other.
- Blood patterns in the stairwell indicated that both victims were shot at or near this location. Joshua Humiston’s head wound left a significant amount of blood on the floor, while Mark sustained multiple gunshot wounds to his back and shoulder, indicating he may have been shot while trying to shield his son or escape.
The Hallway near the Children’s Bedrooms
- Katheryn Humiston. (7-year-old sister) was found slumped in the hallway. Autopsy results later confirmed that she was shot from left to right across her head, with the bullet penetrating her brain and causing fatal injuries. Blood spatter in the hallway and on the walls indicated that the shooting occurred at close range.
- Near the hallway, investigators found bullet holes in the walls, suggesting additional shots had been fired during the attack, possibly as the children attempted to flee.
The Master Bedroom and Ensuite Bathroom
- Sarah Humiston (mother) was found in the ensuite bathroom of the master bedroom. Her body was folded forward on the floor, with multiple gunshot wounds to her head and face.
- The bathroom doorframe had been splintered, indicating that it was likely locked during the attack and had been forced open from the outside. Investigators found several handprints and blood stains on the back of the bathroom door, suggesting a struggle may have occurred.
- A 9mm shell casing was found near the bathroom sink. Investigators noted that blood from Sarah’s wounds had pooled around her body and extended toward the toilet, indicating she was shot multiple times while trying to escape or hide.
Staged Crime Scene and Deceptive Evidence
One of the most significant findings was the deliberate staging of the crime scene. Andrew attempted to shift the blame for the murders onto his 13-year-old brother, Benjamin Humiston. Investigators found Benjamin Humiston’s body positioned in such a way that it appeared he had killed the family and then committed suicide.
- The Glock pistol was placed in Benjamin Humiston’s hand, suggesting that he was the shooter. However, forensic analysis quickly revealed several inconsistencies:
- No blood transfer was found on the pistol or in Benjamin Humiston’s hand, indicating that he likely did not fire the weapon.
- Ballistics analysis showed that the bullet trajectories did not align with a self-inflicted gunshot wound.
- Stippling (burn marks from close-range shots) was absent around some of the wounds, meaning the shots were fired from more than 24 inches away, further contradicting the murder-suicide theory.
These findings confirmed that the scene had been manipulated to frame Benjamin Humiston as the perpetrator.
Bullet Casings and Ballistics Evidence
- Multiple 9mm shell casings were found throughout the home, with several located in the basement hallway near the children’s rooms. Investigators recovered spent bullets from walls, floors, and furniture, as well as from the victims’ bodies during autopsy.
- The Glock pistol used in the crime matched the caliber and casings found at the scene. Forensic experts confirmed that Andrew had access to the Glock through the gun lockbox near the front door, which only he knew the combination for.
Survivor’s Account and Escape
B.A.H., the 11-year-old sister, provided crucial details about the sequence of events. During her interview with forensic child investigators, she recounted the following:
- She and her younger sister, Katheryn Humiston., were sleeping in their shared bedroom when they were awakened by gunshots.
- B.A.H. saw Andrew enter the room with their father’s silver Glock pistol and shoot both her and Katheryn Humiston. She was hit in the hand and neck but survived by playing dead.
- After Andrew left the room, she climbed out of the “fire window” and ran to the Dennis family home, where she told Bradley Dennis that her family had been murdered.
B.A.H.’s testimony provided critical insight into Andrew’s intent, confirming that he systematically killed the family and attempted to cover up his actions by staging the crime scene.
Autopsies and Medical Findings
The autopsies performed on October 22 and 23, 2024, revealed:
- Mark Humiston (Father):
- Four gunshot wounds, including two to the back and one to the neck.
- Evidence of aspirated blood in his lungs, suggesting he survived briefly after being shot.
- Joshua Humiston (9-year-old Brother):
- Single gunshot wound to the forehead, with the bullet exiting the back of the skull.
- Blood found in his lungs indicated he also lived for a short time after being shot.
- Katheryn Humiston. (7-year-old Sister):
- Shot from left to right across her skull, causing brain injuries.
- Bone fragments and brain lacerations contributed to her immediate death.
- Sarah Humiston (Mother):
- Multiple gunshot wounds, including one to the cheek.
- Found folded forward in the ensuite bathroom with blood spatter evidence suggesting close-range shots.
- Benjamin Humiston (13-year-old Brother):
- Two gunshot wounds, staged to appear as self-inflicted.
- No scorching or stippling around the wounds, indicating shots were fired from a distance.
The autopsy findings confirmed that all five victims were murdered, and the attempt to frame Benjamin Humiston was fabricated.
Psychological Profile and Motive
Andrew Jacob Humiston, during his 911 call, mentioned that fear of getting in trouble for looking at pornography and failing tests at school might have motivated his actions. However, the level of planning and the deliberate staging of the scene point to a deeper psychological disturbance. Investigators noted that family dynamics and personal stress may have played a role in triggering this tragic event.
Final Observations by Investigators
The investigation concluded that:
- The murders were premeditated, with Andrew deliberately targeting each family member.
- The crime scene was staged to mislead investigators and frame Benjamin Humiston as the perpetrator.
- Andrew acted alone, using the Glock pistol from the family lockbox to carry out the murders.
- B.A.H.’s survival and testimony provided the key to unraveling the case and establishing Andrew’s culpability.
Summary of Crime Scene and Investigation Findings
The investigation revealed a systematic and deliberate mass killing, committed by Andrew Jacob Humiston, who attempted to conceal his involvement through staging and deception. The combination of forensic evidence, autopsy reports, and survivor testimony painted a clear picture of premeditated murder. Andrew’s actions were not only violent but also manipulative, as evidenced by his attempt to shift blame onto his deceased brother.
The severity and complexity of the crime underscore the importance of the domestic violence charges and the aggravating factors attached to each count. Andrew now faces 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree and 1 count of Attempted Murder in the First Degree, ensuring that the legal system will hold him accountable for these heinous acts.
Autopsy Results
The autopsies of the Humiston family members were conducted at the King County Medical Examiner’s Office on October 22 and 23, 2024. Forensic pathologists carefully examined the remains to determine the precise cause of death, bullet trajectories, and whether any injuries were self-inflicted, as well as to uncover additional evidence regarding the manner of death.
The autopsy reports provided crucial insights that disproved the staged crime scene suggesting that Benjamin Humiston (13-year-old brother) was the perpetrator. Each victim’s injuries pointed to deliberate execution-style shootings, supporting the prosecution’s theory of premeditated, coordinated murders carried out by Andrew Jacob Humiston.
1. Mark Humiston (Father)
- Cause of Death: Multiple gunshot wounds.
- Manner of Death: Homicide.
- Details of Injuries:
- Wound 1: A grazing gunshot wound to the left shoulder.
- Wound 2: A penetrating gunshot wound to the left armpit, which traveled through soft tissue.
- Wound 3: A penetrating gunshot wound to the lower right back.
- Wound 4: A fatal penetrating gunshot wound to the neck.
- Additional Findings:
The autopsy revealed aspirated blood in Mark’s lungs, indicating that he was alive for a brief period after being shot. The placement of the wounds suggests that Mark was likely shot from behind, indicating he may have been trying to escape or protect his children. Three projectiles were recovered from his body during the autopsy.
Conclusion: Mark’s injuries were consistent with a targeted, deliberate attack, intended to ensure that he could not intervene in the ongoing assault on other family members.
2. Joshua Humiston (9-Year-Old Brother)
- Cause of Death: Single gunshot wound to the head.
- Manner of Death: Homicide.
- Details of Injuries:
- A perforating gunshot wound entered Joshua Humiston’s forehead and exited through the back of his skull, indicating the shot was fired at close range.
- Additional Findings:
Blood was found in Joshua Humiston’s lungs, indicating that he may have been conscious for a brief period after being shot, though severely injured. The entry and exit wounds suggest the use of the Glock pistol at close range, and there were no signs of defensive injuries, indicating the attack was sudden and unexpected.
Conclusion: Joshua Humiston’s death was consistent with an execution-style killing, likely part of a deliberate plan to eliminate all witnesses.
3. Katheryn Humiston. (7-Year-Old Sister)
- Cause of Death: Single gunshot wound to the head.
- Manner of Death: Homicide.
- Details of Injuries:
- A penetrating gunshot wound entered the left side of Katheryn Humiston.’s skull and traveled laterally across the top of her head. The bullet caused fractures to the skull and lacerations in the brain tissue, resulting in immediate death.
- Additional Findings:
Bone fragments from the impact were driven into her brain, and aspirated blood was found in her lungs, suggesting she lived momentarily after the injury. Blood spatter on the floor and walls of the hallway aligned with the autopsy findings, indicating that Katheryn Humiston. was shot at close range while standing or moving through the hallway.
Conclusion: The fatal shot to Katheryn Humiston.’s head was intentional and executed with precision, consistent with the respondent’s deliberate actions to ensure the death of all family members.
4. Sarah Humiston (Mother)
- Cause of Death: Multiple gunshot wounds.
- Manner of Death: Homicide.
- Details of Injuries:
- Wound 1: A perforating gunshot wound entered behind Sarah’s right ear and exited through her left cheek.
- Wound 2: A penetrating gunshot wound entered her left temple and lodged behind her eye.
- Additional Findings:
Blood pooling on the bathroom floor suggested that Sarah was shot multiple times at close range while attempting to hide. Investigators found her body folded forward near the toilet, suggesting she may have collapsed mid-stride or was crouching when she was shot. The angle of the bullet trajectories suggests she was shot from above, possibly as she attempted to shield herself.
Conclusion: Sarah’s death was consistent with a planned and targeted attack, indicating she was intentionally killed in the master bathroom, where she may have sought refuge.
5. Benjamin Humiston (13-Year-Old Brother)
- Cause of Death: Multiple gunshot wounds.
- Manner of Death: Homicide (with evidence of staging).
- Details of Injuries:
- Wound 1: A penetrating gunshot wound to the left cheek. The bullet traveled from left to right, passing through his brain and lodging in his skull.
- Wound 2: A second penetrating wound entered the back of his right ear.
- Additional Findings:
No stippling or scorching was observed around the entry wounds, indicating that the shots were fired from more than 24 inches away, ruling out the possibility of self-inflicted injuries. The lack of blood transfer on the Glock pistol further supported the conclusion that Benjamin Humiston was not the shooter. The placement of the wounds suggested he was deliberately killed and then staged to appear as though he had committed the murders and taken his own life.
Conclusion: Benjamin Humiston’s death was part of a calculated attempt to deceive investigators. The wounds and physical evidence confirmed that Andrew Humiston staged the scene to frame Benjamin Humiston for the murders.
6. B.A.H. (11-Year-Old Sister, Survivor)
- Injuries:
- Gunshot wound to the hand.
- Gunshot wound to the neck.
- Details of Injuries:
The gunshot wound to B.A.H.’s neck narrowly missed major arteries but caused significant bleeding. She was also shot in the hand, which investigators believe may have been a defensive wound as she attempted to shield herself from the attack.
- Additional Findings:
B.A.H. survived by pretending to be dead after being shot. Her quick thinking allowed her to escape through the fire window and seek help from a neighbor. Medical records indicate that she required emergency treatment for blood loss but was in stable condition at the time of the interview with detectives.
Conclusion: B.A.H.’s survival was a critical element in unraveling the truth behind the crime. Her injuries were consistent with deliberate attempts to kill her, supporting the charge of Attempted Murder in the First Degree.
Summary of Autopsy Findings
The autopsy reports confirmed the following:
- All five victims—Mark, Sarah, Joshua Humiston, Katheryn Humiston., and Benjamin Humiston—died from gunshot wounds inflicted by Andrew Humiston.
- The absence of stippling on the wounds and the location of spent casings ruled out the staged narrative of a murder-suicide by Benjamin Humiston.
- The presence of aspirated blood in several victims indicated they were conscious for brief moments after being shot.
- B.A.H.’s survival and her ability to recount the events were crucial in exposing the truth and ensuring Andrew could not maintain his fabricated story.
Conclusion
The forensic evidence and autopsy results conclusively established that Andrew Jacob Humiston acted with premeditated intent to kill his family. His attempt to stage the crime scene by framing his brother Benjamin Humiston was carefully planned but ultimately exposed by forensic inconsistencies. The surviving victim, B.A.H., played a critical role in providing eyewitness testimony that confirmed Andrew’s involvement and dismantled his false narrative.
These findings, combined with the survivor’s testimony, supported the prosecution’s charges of 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree and 1 count of Attempted Murder in the First Degree. The crime scene and autopsy evidence revealed a systematic and calculated plan to eliminate the entire family and mislead investigators through deceitful staging.
Sentencing Guidelines and Potential Outcomes
The outcome of the case will depend on whether the court decides to try Andrew as an adult. Here are the two potential scenarios:
- Tried as an Adult:
- Aggravated Murder: Each count carries a mandatory life sentence without parole for adult offenders.
- Attempted Murder: A conviction would result in a potential life sentence, though parole eligibility could be granted.
- Firearm Enhancements: An additional sentence enhancement for each offense involving a firearm, typically 5 to 10 years, could apply.
- Tried as a Juvenile:
- The court may impose juvenile sentencing guidelines, which often focus on rehabilitation and limit incarceration periods. However, given the gravity of the crimes, the court could impose a blended sentence, meaning Andrew could be held in a juvenile facility until he reaches adulthood, at which point the case could transfer to adult court.
Prosecutor’s Recommendations
The Prosecuting Attorney, Leesa Manion, has formally charged Andrew with:
- 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence)
- 1 count of Attempted Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence)
Given the severity of the offenses and the aggravating factors involved, the prosecution is likely to pursue adult criminal charges to ensure that Andrew faces the maximum penalties. The prosecution may argue that the level of planning, the deliberate targeting of multiple family members, and the attempt to deceive investigators warrant life imprisonment without parole.
Conclusion
The charges against Andrew Jacob Humiston reflect the most severe criminal offenses under Washington law. The aggravated nature of the murders, combined with the use of a firearm and the deliberate staging of the crime scene, leaves little room for leniency. The fact that the crimes were committed against family members further enhances the gravity of the case under domestic violence statutes.
Whether tried as a juvenile or an adult, Andrew faces significant legal consequences. The prosecution’s recommendation to charge him with aggravated murder and attempted murder, combined with the use of a firearm, suggests that the state will seek the harshest possible penalties under the law.
Next Steps
The legal proceedings for Andrew Jacob Humiston will now follow a series of structured steps. These steps are crucial in determining how the case will progress, whether the juvenile will be tried as an adult, and what potential sentencing guidelines will apply if he is found guilty.
Given the severity and complexity of the case—marked by multiple murders, attempted murder, and the staging of the crime scene—the legal process will likely involve extensive legal arguments, psychological evaluations, and judicial oversight to ensure justice is served. Below is a detailed breakdown of the steps that are likely to follow:
1. Initial Hearing and Arraignment
- What Happens: Andrew will be formally presented before a judge at the King County Juvenile Court (or adult criminal court if transferred). During the arraignment, the prosecution will read the charges aloud, and Andrew will enter a plea (likely “not guilty”).
- Possible Outcomes:
- The judge will decide on detention status, including whether Andrew will remain in custody or be allowed supervised release pending trial. Given the nature of the crimes, he will likely remain detained in juvenile custody or a secure detention center.
- If the case proceeds in adult court, bail may be denied due to the risk to public safety and the seriousness of the charges.
2. Juvenile vs. Adult Court Decision
- Judicial Transfer Hearing: The prosecution will likely request that Andrew be tried as an adult, given the premeditated and aggravated nature of the crimes. The court will consider several factors, including:
- The severity of the offense (5 counts of Aggravated Murder and 1 count of Attempted Murder).
- Andrew’s age (15 years old) and whether he demonstrates the maturity to understand the nature and consequences of his actions.
- Psychological and psychiatric evaluations (which will assess whether Andrew has underlying mental health issues or is capable of rehabilitation).
- The intent behind the crimes, especially the effort to stage the scene and manipulate investigators.
- Possible Outcomes:
- Adult Court Transfer: If transferred to adult court, Andrew will face the possibility of life imprisonment without parole and firearm-related sentencing enhancements.
- Juvenile Jurisdiction: If the judge decides the case remains in juvenile court, the focus will shift to rehabilitation. In Washington, juveniles are typically not given life sentences without parole, though blended sentences (continuing into adulthood) may be imposed.
3. Psychological Evaluation
- What Happens: The defense may request a mental health evaluation to determine whether Andrew was suffering from any psychological disorders at the time of the offense. Evaluators will assess:
- Cognitive ability and mental competence to stand trial.
- Any history of mental illness or emotional disturbances that might mitigate Andrew’s culpability.
- Whether stressors (such as school failure or family dynamics) influenced his actions.
- Possible Outcomes:
- If the evaluation reveals a mental health condition, the defense may argue for a diminished capacity defense, aiming for a lesser charge.
- If no significant mental illness is found, the prosecution’s argument for premeditation and intentional acts will be strengthened.
4. Discovery and Pre-Trial Motions
- What Happens: Both the prosecution and defense will engage in the discovery process, exchanging evidence, including:
- 911 call recordings.
- Forensic reports (ballistics, blood spatter analysis, etc.).
- Autopsy findings for the five victims.
- Witness statements, especially from the surviving sibling, B.A.H..
- Digital evidence, such as phone records and school records.
- Pre-Trial Motions:
- The defense may file motions to suppress certain evidence (such as the 911 call) or challenge the admissibility of forensic evidence.
- The prosecution may file motions to admit prior statements made by Andrew or request expert testimony to establish premeditation and the intent behind staging the scene.
- Possible Outcomes:
- The judge will rule on the admissibility of evidence, which will significantly impact the course of the trial.
5. Plea Bargain Negotiations (Optional)
- What Happens: Given the overwhelming evidence against Andrew, the defense may consider a plea deal to avoid the possibility of life imprisonment without parole.
- The prosecution could offer a plea agreement, reducing the charges to murder in the second degree or manslaughter, contingent upon Andrew’s cooperation.
- Possible Outcomes:
- If a plea agreement is reached, Andrew could receive a reduced sentence, potentially with eligibility for parole.
- If no plea deal is accepted, the case will proceed to trial.
6. Trial Proceedings
- What Happens: If the case goes to trial, it will be a jury trial if heard in adult court, or a bench trial (before a judge) if it remains in juvenile court. The trial will involve:
- Opening statements by the prosecution and defense.
- Presentation of evidence by the prosecution, including:
- Testimony from B.A.H., the surviving sibling.
- Expert witnesses on forensics and ballistics.
- Psychological experts, if mental health becomes a factor.
- Defense strategy, which may include arguments related to mental health, stress, or diminished capacity.
- Closing arguments and jury deliberation (in adult court) or a judicial ruling (in juvenile court).
- Possible Outcomes:
- Guilty Verdict: Andrew could be convicted of aggravated murder and attempted murder.
- Not Guilty Verdict: If the defense successfully introduces doubt, Andrew could be acquitted (although this outcome seems unlikely given the evidence).
- Mistrial or Hung Jury: If the jury cannot reach a unanimous decision, the prosecution may retry the case.
7. Sentencing
- What Happens: If Andrew is found guilty, a sentencing hearing will follow.
- In Adult Court: Sentencing will likely involve mandatory life imprisonment without parole for each count of aggravated murder. However, the judge may consider consecutive or concurrent sentences.
- In Juvenile Court: Sentencing may focus on rehabilitation, with a potential blended sentence. Andrew could serve time in a juvenile detention facility until age 21, after which he may be transferred to adult prison if the court deems it necessary.
8. Appeals Process (If Convicted)
- What Happens: If Andrew is convicted, the defense has the right to appeal the verdict or the sentence. Appeals may focus on:
- Errors during trial (e.g., improper admission of evidence).
- Inadequate legal representation.
- Misapplication of juvenile or adult sentencing guidelines.
- Possible Outcomes:
- Successful Appeal: The conviction or sentence could be overturned or modified.
- Unsuccessful Appeal: The original conviction and sentence will stand.
9. Long-Term Impact and Rehabilitation Options (If Sentenced as a Juvenile)
- If Andrew remains under juvenile jurisdiction, the focus will be on rehabilitative programs. This may include:
- Psychological counseling.
- Educational and vocational programs to prepare him for eventual reintegration into society.
- Behavioral therapy focused on addressing any emotional or mental health issues.
- However, if Andrew is transferred to adult prison, the focus will shift toward punishment and containment, with limited access to rehabilitative services.
Summary of Next Steps
The next steps in this case are critical in determining whether Andrew will be tried as an adult or a juvenile and whether the legal system will focus on punishment or rehabilitation. With overwhelming evidence of premeditation, intent, and manipulation, the prosecution will likely push for a transfer to adult court and seek the maximum penalties.
The outcome of the psychological evaluation, legal motions, and trial proceedings will shape the ultimate resolution of this case. Whether through a trial or plea bargain, the legal system will aim to ensure that justice is served for the victims and the surviving family member, B.A.H.
Summary and Legal Recommendation
Given the severity and premeditated nature of the crimes, the prosecution recommends the following:
- 5 counts of Aggravated Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence)
- 1 count of Attempted Murder in the First Degree (Domestic Violence)
The case will proceed under the juvenile division of the King County Superior Court. The findings point toward a systematic and deliberate act of familial homicide with a failed attempt to mislead law enforcement through staged evidence.
 >
> >
> >
>



 >
> >
> >
>






















 >
> >
>